-
- Maintain a healthy weight: Excess body fat can increase estrogen levels, contributing to the development of gynecomastia. Maintaining a stable weight through a healthy diet and exercise can help minimize the risk of developing this condition.
- Avoid or limit alcohol and drugs: Alcohol and certain medications, such as anabolic steroids, marijuana, and opioids, can interfere with hormone production and regulation, leading to an increased risk of developing gynecomastia. Avoiding or limiting these substances can help reduce the risk of developing this condition.
- Review medications: If you are taking medicines that list gynecomastia as a side effect, talk to your healthcare provider about alternatives or possible adjustments to your treatment plan.
- Monitor your hormone levels: If you are at risk for hormonal imbalances, such as during puberty or in older age, monitoring your hormone levels can help detect any changes that may contribute to the development of gynecomastia.
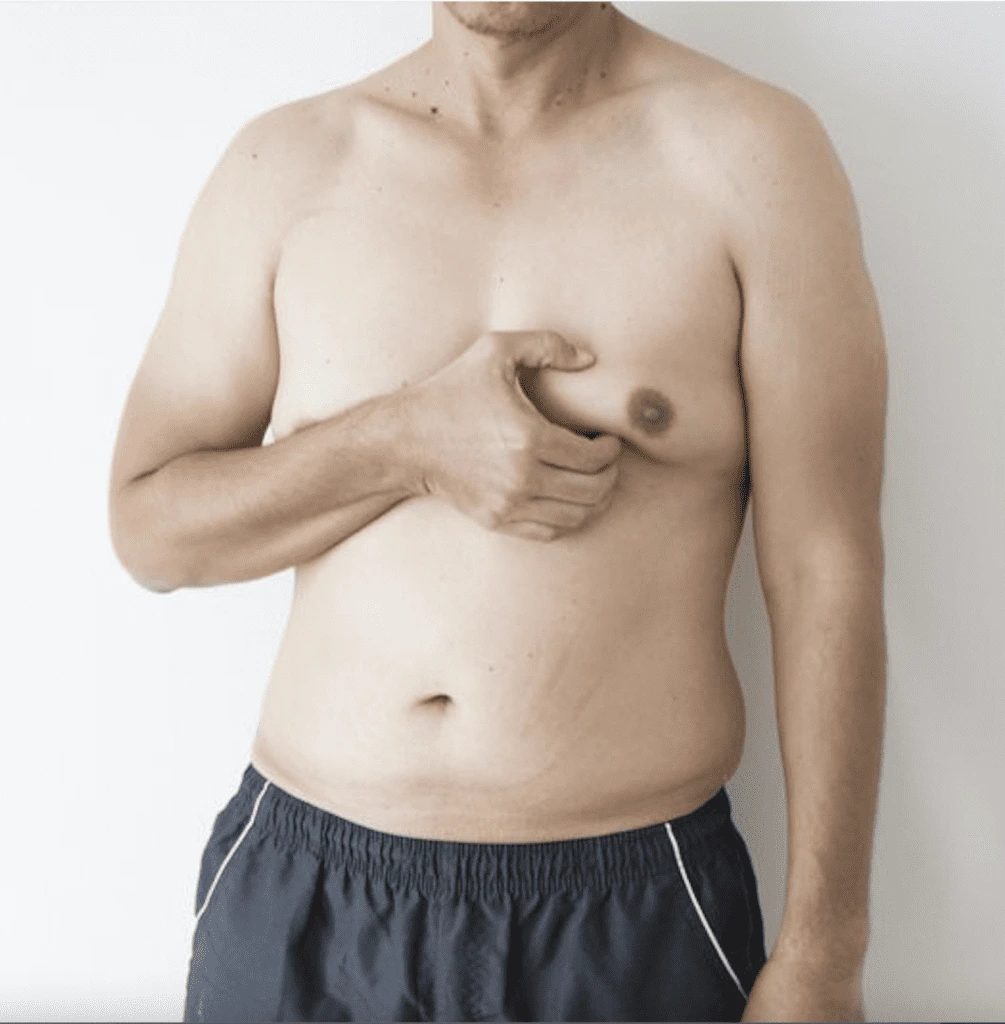
- Get medical attention immediately. If you notice signs of gynecomastia, such as tenderness or swelling of the breasts, seek medical attention immediately. Early diagnosis and treatment can keep the condition from worsening and lessen emotional and physical stress.
Importance of early intervention
Early intervention for gynecomastia is crucial for several reasons. First and foremost, gynecomastia can cause physical inconvenience and emotional suffering, particularly in young males who may feel self-conscious about their appearance.
In addition to reducing physical and emotional discomfort, early intervention can prevent the condition from worsening. Unfortunately, in some cases, gynecomastia can cause the breast tissue to become permanently enlarged, making it more difficult to treat later.
Furthermore, early intervention can also help rule out the possibility of breast cancer. While gynecomastia is not a type of cancer, the symptoms can sometimes be mistaken for breast cancer, particularly in older men. By seeking prompt medical attention, a healthcare provider can perform tests to rule out severe underlying conditions and provide appropriate treatment options before permanent damage occurs.
Living with Gynecomastia
Living with gynecomastia can be challenging, both physically and emotionally. It can cause physical discomfort and self-consciousness, particularly in social situations where the chest is exposed. However, there are strategies to cope that can assist people in managing this condition successfully.
Coping strategies for those with gynecomastia
-
- Wear proper clothing: Wearing clothes that fit correctly and flatter the body shape can help individuals with gynecomastia feel more confident and comfortable. Compression shirts or undershirts can also help minimize the appearance of swollen breast tissue.
-
- Seek medical treatment: Medical treatment can help manage the physical symptoms of gynecomastia, such as breast pain or tenderness. It can also help identify and address any underlying medical conditions causing this condition.
-
- Stay active: Regular exercise can help improve overall physical health and self-esteem. It can also help individuals maintain a healthy weight and reduce excess body fat, which can contribute to gynecomastia.
Importance of emotional support
It is essential to have emotional support when living with gynecomastia. Family and friends can provide a listening ear and offer encouragement and reassurance. Counseling and support groups can also be a safe place to talk about your issues and connect with others who are experiencing similar experiences.
Tips for building self-esteem
-
- Focus on positive qualities: Instead of fixating on the appearance of the chest, focus on positive attributes and strengths. Celebrate personal achievements and talents.
- Self-care. It is about taking good care of oneself physically and mentally to improve self-esteem. Examples include relaxing in a bath, walking, or even reading books.
- Seek professional help: If self-esteem issues persist, seek a mental health professional. They can guide and support in building self-esteem and managing related anxiety or depression.
Managing Gynecomastia
Managing gynecomastia can involve lifestyle changes, medical treatments, and surgery. Individuals with gynecomastia can develop a treatment plan tailored to their needs by working with a healthcare provider.
Lifestyle changes to manage gynecomastia
-
- Maintain a healthy weight: Excess body fat can increase estrogen levels, contributing to the development of enlarged breasts. Maintaining an ideal weight by eating healthy and regularly exercising will lower the chance of developing this condition.
- Avoid or limit alcohol and drugs: Alcohol and certain medications, such as anabolic steroids, marijuana, and opioids, can interfere with hormone production and regulation, leading to an increased risk of developing gynecomastia. Avoiding or limiting these substances can help reduce the risk of developing this condition.
Medical treatments for gynecomastia
-
- Hormone therapy: If hormonal imbalances contribute to the development of gynecomastia, hormone therapy may be recommended and can involve medications to block estrogen production or increase testosterone levels.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as tamoxifen or raloxifene, can help reduce the size of breast tissue in men with gynecomastia.
- Breast Reduction Surgery for Gynecomastia via Liposuction: Liposuction is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that removes excess fat from the breast area. It is particularly effective for men with gynecomastia caused by excess fat tissue. JustGoLipo offers minimally invasive chest liposuction services for gynecomastia. Dr. Singh, a highly skilled and experienced body contouring physician, performs these procedures using the latest liposuction techniques and technologies to achieve natural-looking and satisfying results. JustGoLipo is a top choice for those seeking chest liposuction for gynecomastia.